-
MINISTRY
-
FUNCTIONS
- Economic Policy
-
Agriculture
- Agrarian policy
- Agrarian policy Agrarian policy
- Agro-processing
- Agro-processing Agro-processing
- Animal breeding
- Animal breeding Animal breeding
- Veterinary medicine
- Veterinary medicine Veterinary medicine
- Plant cultivation
- Plant cultivation Plant cultivation
- Phytosanitary
- Phytosanitary Phytosanitary
- Agricultural cooperation
- Agricultural cooperation Agricultural cooperation
- Fish farming
- Fish farming Fish farming
- Food security
- Food security Food security
- Organic agriculture
- Organic agriculture Organic agriculture
- Public Investment
- Investment Policy
- Free Economic Zones
- Industrial Policy
- Business Environment
- Small and medium-sized entrepreneurship
- International Cooperation
- Armenia - European Union
- Armenia-EAEU
- Armenia - WTO
- Trade and Market Regulation
- Tourism
- Capital market
- Quality infrastructure
- Сtrategic sectors
- Licensing, permits
- Intellectual Property
-
PROJECTS
- State Support Programs for Agriculture
- Economy modernization program
- Infrastructure for investment assistance event
- State support program for issuance and rating
- The state support program for commercial companies engaged in the production of economically complex products
- Fee and cost reimbursement program for drug registrations and re-registration examinations
- Program for Compensation of Costs of Clinical Trials and Bioequivalence Studies in the Republic of Armenia
-
INFORMATION
-
MEDIA CENTER
- CONTACTS
- Economic Policy
- Agriculture
- Public Investment
- Investment Policy
- Free Economic Zones
- Industrial Policy
- Business Environment
- State Support Programs for Agriculture
- Economy modernization program
- Infrastructure for investment assistance event
- State support program for issuance and rating
- The state support program for commercial companies engaged in the production of economically complex products
- Fee and cost reimbursement program for drug registrations and re-registration examinations
- Program for Compensation of Costs of Clinical Trials and Bioequivalence Studies in the Republic of Armenia
Home
FUNCTIONS
Small and medium-sized entrepreneurship is one of the most important factors in increasing the competitiveness of the Armenian economy, ensuring inclusiveness and sustainable development. The 2019 program of the Government of the Republic of Armenia largely emphasizes the SME development, which is considered a pre-requisite for inclusive economic growth.
In 2011, the definition of SME in the Republic of Armenia in terms of the average payroll number of employees was harmonized with the SME definition in the EU member states, according to which the SME entities for administrative purposes are classified according to the criteria presented below.
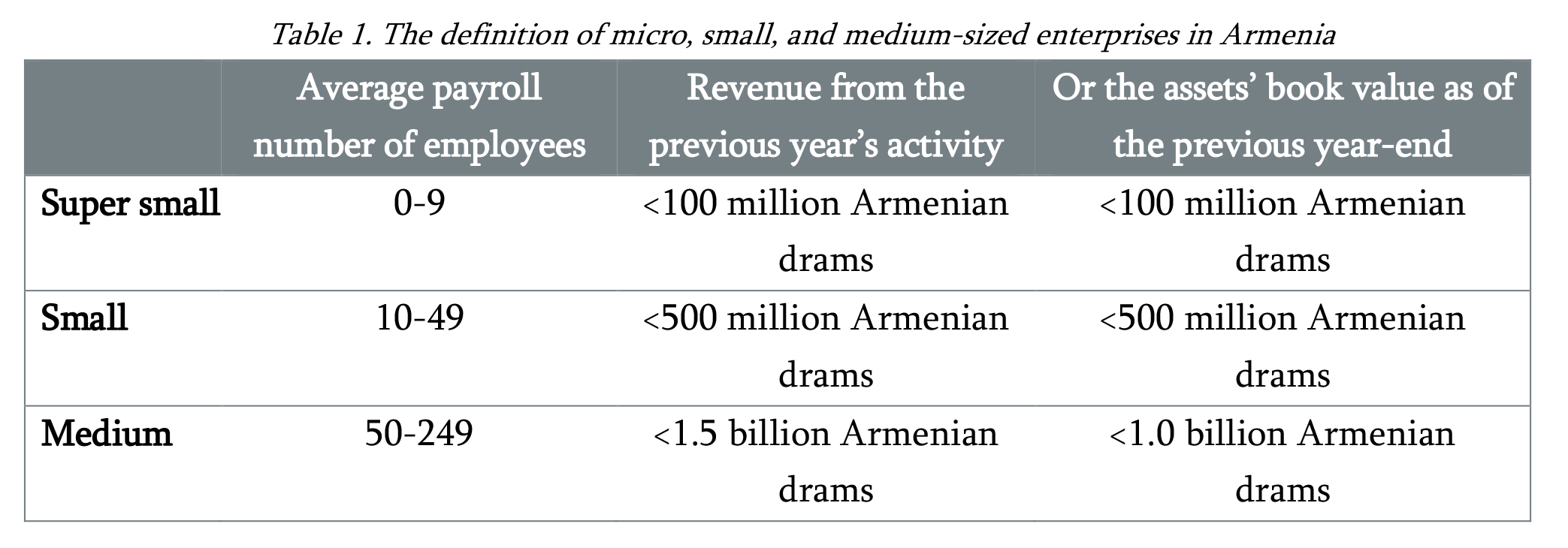
In 2018, within the framework of the “Support to SME Development in Armenia” program, for the first time ARMSTAT prepared and published the “SME in the Republic of Armenia․ 2018” newsletter. The newsletter summarizing 2018 activities was continuously published in 2019, the main indicators of which are presented below. The publication uses the SME classification exclusively in terms of the number of employees, according to the internationally accepted criteria for the SME classification for statistical purposes.
In 2018, the share of the added value produced by super small, small, and medium-sized enterprises within the GDP of the RA total economy was 23.6%.
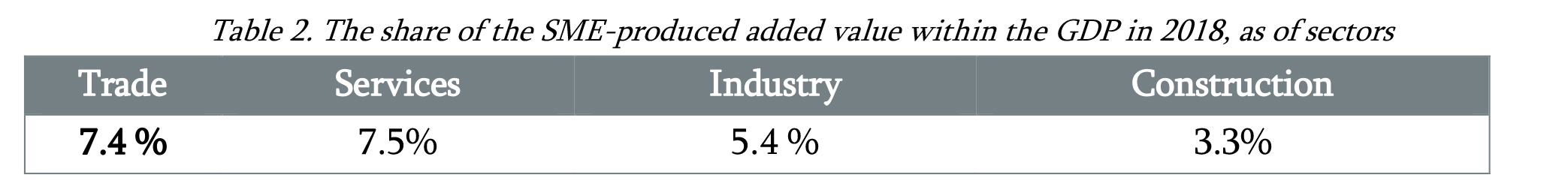
In 2018, the number of SME entities operating in the Republic of Armenia was 68,780, of which only 126 (about 0.18%) were classified as large businesses. 52.1% of SMEs operate in Yerevan.
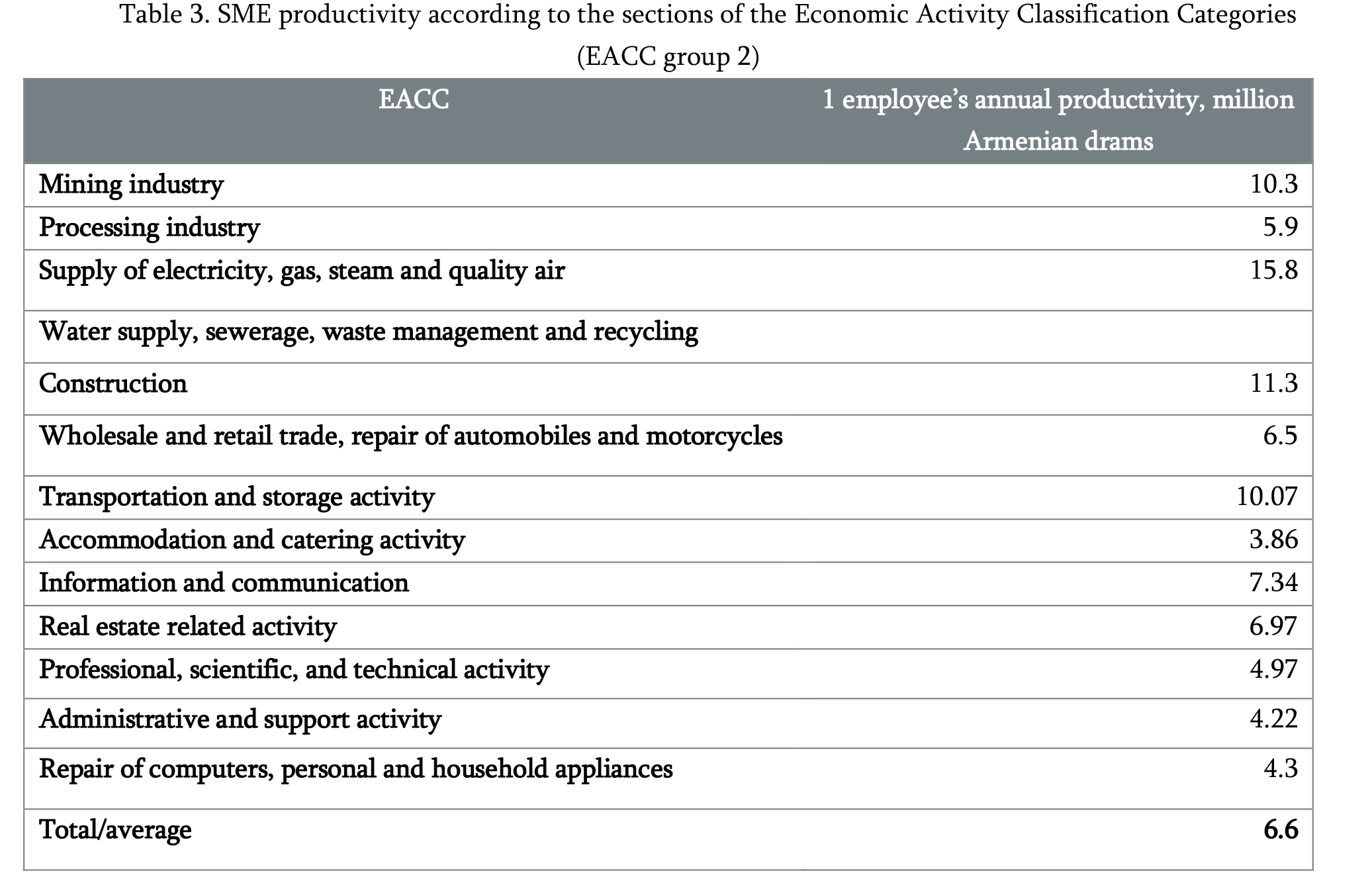
The added value produced per employee of the SME sector in Armenia in 2018 amounted to about 6.66 million Armenian drams (about 13,700 US dollars) annually, whereby in large companies it amounted to 9.55 million Armenian drams (about 19,700 US dollars). The table below presents the performance of SME productivity by sectors in 2018․
The average density of SMEs per 1,000 population in Armenia is low at 23.1. More than half of SMEs operate in Yerevan, where the density of SMEs per 1,000 inhabitants is 33, while in the Marzes the same indicator is significantly lower. Among the SMEs outside the area of Yerevan, Kotayk Marz stands out, where 8.6% of SMEs are located, and the SME density per 1,000 inhabitants is 23.4 [ARMSTAT, Small and medium-sized entrepreneurship in the Republic of Armenia, 2019].
In 2018, the number of companies being established per 1,000 inhabitants in Armenia was 9.8. According to the WB report, this indicator reaches 30 in high-middle-income countries. Presently the given indicator of Armenia corresponds to the one of low-middle income countries.
The following strategic directions are emphasized by the Government of the Republic of Armenia to strengthen the SME sector and increase competitiveness in the Republic of Armenia:
- Increasing the accessibility of financial resources,
- Capacity building of SMEs and development of business culture,
- Ensuring the accessibility of markets for SMEs,
- Providing a favorable institutional and legal environment for SME development.
SMALL AND MEDIUM-SIZED ENTREPRENEURSHIP DEVELOPMENT STRATEGY 2020-2024
During its session on August 27, 2020, the Government of the Republic of Armenia approved the Small and Medium-sized Entrepreneurship Development Strategy for 2020-2024 and its associated action plan for 2020-2022 developed by the RA Ministry of Economy.
The goal of the strategy is to create a favorable environment for SMEs of the Republic of Armenia through development of entrepreneurial skills, implementation of ideas, increasing the competitiveness, which will allow to provide SMEs with access to domestic and foreign markets.
The target measures of the strategy are aimed at increasing the accessibility of financial resources for SMEs, capacity building, as well as formation of institutional and legal environment necessary for promotion of entrepreneurial culture.
At the effect of implementation of the measures defined by the strategy, it is planned to facilitate the growth of the SME productivity, increasing the productivity by 3% in 2020-2023, and by 7.5% in 2024. In particular, the added value produced by one employee in SMEs in 2024 will amount to 12 million AMD, which is almost doubling the same indicator in 2018 (6.7 million AMD in 2018).
At the effect of the targeted activities stipulated by the strategy, the number of people employed in SMEs will increase by an annual average of 2.5%.
In order to mitigate the effects of the pandemic, more attention was paid to improving the mechanisms of the bankruptcy process and the second chance, overcoming additional difficulties related to access to financing, the need of SMEs engagement in large value chains. At the effect of the implemented activities, not only will the productivity of SMEs significantly improve and the number of employed will increase, but also, due to the transferred skills and improved environment, engagement in an entrepreneurial activity can become an alternative to work abroad, lost jobs, and recovery of income.
SME state support annual programs
"State support to the implementation of the statutory objectives of the SME DNC of Armenia" 2017 program(available in Armenian)
Support for SMEs 2014 program (available in Armenian)
Support for SMEs 2015 program (available in Armenian)
Support for SMEs 2016 program (available in Armenian)
Small and Medium Entrepreneurship
-
Hot line
* Hot line operates on weekdays (Monday-Friday) from 09:00 to 18:00.
- BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT
- (+374 11) 597 539
- TOURISM
- (+374 11) 597 157
- QUALITY INFRASTRUCTURES
- (+374 11) 597 167
- PRODUCT LABORATORY TESTING
- (+374 11) 597 166